Getting Started¶
================================================
____ _
/ __ \(_)___ ____ ____ ____ ___ _____
/ / / / / __ \/ __ `/ _ \/ __ \/ _ \/ ___/
/ /_/ / / /_/ / /_/ / __/ / / / __(__ )
/_____/_/\____/\__, /\___/_/ /_/\___/____/
/____/
================================================
Introduction¶
Diogenes is a a Python library and workflow templet for machine learning. Principally it wraps sklearn providing enhanced functionality and simplified interface of often used workflows.
Example¶
%matplotlib inline
import diogenes
import numpy as np
Get data from wine quality data set
data = diogenes.read.open_csv_url(
'http://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/machine-learning-databases/wine-quality/winequality-white.csv',
delimiter=';')
Note that data is a Numpy structured array We can use it like this:
data.dtype.names
('fixed acidity',
'volatile acidity',
'citric acid',
'residual sugar',
'chlorides',
'free sulfur dioxide',
'total sulfur dioxide',
'density',
'pH',
'sulphates',
'alcohol',
'quality')
print data.shape
(4898,)
print data['fixed acidity']
[ 7. 6.3 8.1 ..., 6.5 5.5 6. ]
We separate our labels from the rest of the data and turn our labels into binary classes.
labels = data['quality']
labels = labels < np.average(labels)
print labels
[False False False ..., False False False]
Remove the labels from the rest of our data
M = diogenes.modify.remove_cols(data, 'quality')
print M.dtype.names
('fixed acidity', 'volatile acidity', 'citric acid', 'residual sugar', 'chlorides', 'free sulfur dioxide', 'total sulfur dioxide', 'density', 'pH', 'sulphates', 'alcohol')
Print summary statistics for our features
diogenes.display.pprint_sa(diogenes.display.describe_cols(M))
Column Name Count Mean Standard Dev Minimum Maximum
0 fixed acidity 4898 6.85478766844 0.843782079126 3.8 14.2
1 volatile acidity 4898 0.278241118824 0.100784258542 0.08 1.1
2 citric acid 4898 0.334191506737 0.12100744957 0.0 1.66
3 residual sugar 4898 6.39141486321 5.07153998933 0.6 65.8
4 chlorides 4898 0.0457723560637 0.0218457376851 0.009 0.346
5 free sulfur dioxide 4898 35.3080849326 17.0054011058 2.0 289.0
6 total sulfur dioxide 4898 138.360657411 42.4937260248 9.0 440.0
7 density 4898 0.99402737648 0.00299060158215 0.98711 1.03898
8 pH 4898 3.18826663944 0.150985184312 2.72 3.82
9 sulphates 4898 0.489846876276 0.114114183106 0.22 1.08
10 alcohol 4898 10.5142670478 1.23049493654 8.0 14.2
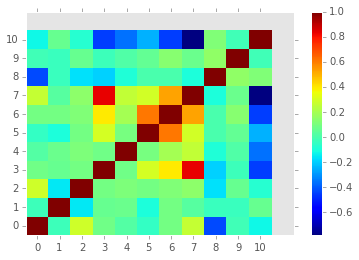
Plot correlation between features
fig = diogenes.display.plot_correlation_matrix(M)
Arrange an experiment trying different classifiers
exp = diogenes.grid_search.experiment.Experiment(
M,
labels,
clfs=diogenes.grid_search.standard_clfs.std_clfs)
trials = exp.run()
/Users/zar1/anaconda/lib/python2.7/site-packages/sklearn/svm/base.py:209: ConvergenceWarning: Solver terminated early (max_iter=1000). Consider pre-processing your data with StandardScaler or MinMaxScaler.
% self.max_iter, ConvergenceWarning)
/Users/zar1/anaconda/lib/python2.7/site-packages/sklearn/svm/base.py:209: ConvergenceWarning: Solver terminated early (max_iter=1000). Consider pre-processing your data with StandardScaler or MinMaxScaler.
% self.max_iter, ConvergenceWarning)
Make a pdf report
exp.make_report(verbose=False)
'/Users/zar1/dssg/diogenes/doc/notebooks/report.pdf'
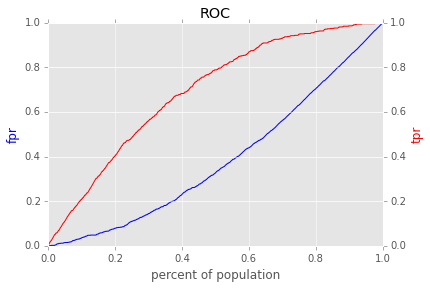
Find the trial with the best score and make an ROC curve
trials_with_score = exp.average_score()
best_trial, best_score = max(trials_with_score.iteritems(), key=lambda trial_and_score: trial_and_score[1])
print best_trial
print best_score
Trial(clf=<class 'sklearn.ensemble.forest.RandomForestClassifier'>, clf_params={'n_estimators': 10, 'max_features': 'log2', 'n_jobs': 1, 'max_depth': 7}, subset=<class 'diogenes.grid_search.subset.SubsetNoSubset'>, subset_params={}, cv=<class 'sklearn.cross_validation.KFold'>, cv_params={})
0.757462757506
fig = best_trial.roc_curve()